Backscatter communication is an emerging wireless technology that allows devices to transmit data by reflecting existing radio frequency (RF) signals, instead of generating their own. This enables ultra-low-power, batteryless communication, making it ideal for IoT sensor nodes.
In the rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, where millions of devices are deployed in smart homes, industries, and cities, backscatter communication offers a sustainable, scalable, and cost-effective solution for continuous data collection.
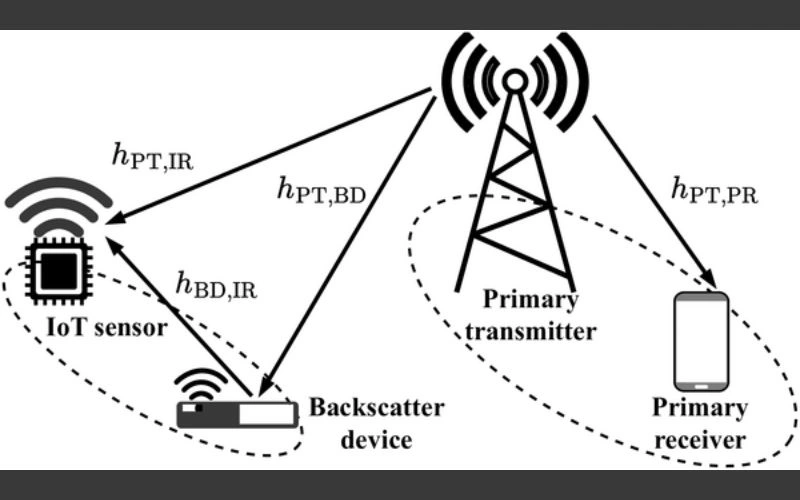
How Backscatter Communication Works in IoT Sensor Nodes
Backscatter communication relies on modulating and reflecting ambient RF signals rather than using a conventional transmitter. Two primary types exist:
- Ambient Backscatter: Uses existing RF sources like WiFi, cellular signals, or TV broadcasts. Devices harvest energy from the environment and reflect the signal to encode data.
- Active Backscatter: Combines a low-power transmitter with reflective elements to improve range and reliability.
The basic mechanism involves a sensor node altering the impedance of its antenna to reflect incoming RF waves. The reflected signal carries data to a reader or gateway. Coupled with energy harvesting circuits, this technique enables completely battery-free operation, extending device lifetime and reducing maintenance costs.
Advantages of Backscatter for IoT Sensor Nodes
Backscatter communication provides several advantages for IoT networks:
- Ultra-Low Power Consumption: Devices can operate on microwatts, making them ideal for energy-constrained environments.
- Battery-Free Operation: Eliminates the need for frequent battery replacements.
- Extended Device Lifetime: Reduced power draw significantly increases operational lifespan.
- Cost-Effective Deployment: Low-power chips and simple circuitry reduce production costs.
- Scalability: Supports dense IoT networks without heavily loading communication channels.
Key Use Cases of Backscatter Communications in IoT Sensor Nodes
Backscatter communication is finding practical applications across multiple industries.
Smart Agriculture
IoT sensor nodes can monitor soil moisture, temperature, and humidity without frequent battery replacements. Backscatter-enabled sensors allow farmers to deploy large-scale networks efficiently, enabling precision agriculture and automated irrigation.
Environmental & Climate Monitoring
Deploying passive sensors in remote forests, rivers, and weather stations reduces maintenance costs. Backscatter sensors can continuously transmit environmental data using ambient RF signals, providing real-time monitoring for climate research.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Sensors
Factories and warehouses leverage backscatter nodes to monitor machinery, track inventory, and detect anomalies. These sensors reduce the need for wiring and battery replacement, supporting predictive maintenance.
Smart Home & Building Automation
Backscatter IoT devices enable smart lighting, HVAC control, and security sensors with minimal power requirements. Their battery-free operation reduces maintenance and ensures uninterrupted automation.
Retail & Inventory Tracking
Passive RFID-like backscatter sensors provide continuous inventory visibility in warehouses and stores. They allow automated tracking of stock levels, reducing human error and operational costs.
Smart Healthcare Wearable Sensors
Medical wearables can monitor heart rate, glucose levels, and activity without bulky batteries. Backscatter communication ensures long-term, non-intrusive patient monitoring.
Logistics & Supply Chain Monitoring
Sensors embedded in packages or shipping containers can relay location, temperature, and vibration data via ambient RF signals. This enables real-time monitoring while maintaining ultra-low energy usage.
Smart Infrastructure (Bridges, Roads, Energy Grids)
Backscatter nodes embedded in critical infrastructure detect structural changes, vibrations, and stress. They provide continuous monitoring without frequent maintenance, reducing safety risks and operational costs.
Research Trends & Latest Innovations in Backscatter IoT 2025

Recent research has focused on enhancing the performance and applicability of backscatter systems:
- Battery-Less Sensor Advancements: Improved energy harvesting circuits now power longer-range devices.
- Hybrid Backscatter: Combining WiFi, Bluetooth, LoRa, and 5G enables extended coverage and flexibility.
- Ultra-Long-Range Backscatter: Innovations in antennas and coding techniques allow reliable communication over hundreds of meters.
- Chip-Level Integration: New ASIC designs integrate backscatter modulation directly into sensor chips, reducing size and cost.
Challenges & Limitations
Despite its advantages, backscatter communication has limitations:
- Range Constraints: Reflected signals have lower power, limiting communication distance.
- Interference: Dense RF environments can cause collisions and reduce reliability.
- Data Rate Issues: Backscatter is generally slower than conventional wireless communication.
- Security Concerns: Passive communication can be intercepted if encryption is not implemented.
Future of Backscatter Communications in IoT (2025–2030)
The future of backscatter-enabled IoT is promising:
- AI-Driven Optimization: Adaptive energy and signal management will improve performance.
- Energy-Adaptive Architectures: Devices will dynamically harvest and use energy efficiently.
- Integration with 6G and Edge Computing: Backscatter nodes will support ultra-dense urban networks.
- Mass Adoption: Cities, industries, and agriculture are expected to increasingly deploy batteryless IoT sensors for large-scale, sustainable networks.
Conclusion
Backscatter communication is transforming IoT sensor networks by providing battery-free, ultra-low-power, cost-effective connectivity. From smart agriculture to healthcare and industrial monitoring, its applications are growing rapidly. As research progresses and hybrid solutions emerge, backscatter-enabled IoT sensor nodes are poised to become a key technology for the next generation of connected devices, supporting sustainable, scalable, and intelligent networks worldwide.
FAQs: Use Cases of Backscatter Communications in IoT Sensor Nodes
1. What is backscatter communication in IoT sensor nodes?
Backscatter communication allows IoT sensor nodes to transmit data by reflecting existing radio signals instead of generating their own, enabling ultra-low power operation and extended battery life.
2. Why is backscatter communication suitable for battery-free IoT sensors?
Because it consumes extremely low energy, backscatter communication enables battery-free or energy-harvesting IoT sensors to operate reliably using ambient RF signals or small harvested power sources.
3. How is backscatter communication used in smart agriculture IoT systems?
In smart agriculture, backscatter-enabled sensors monitor soil moisture, temperature, and humidity while operating maintenance-free for long periods, reducing deployment costs across large farms and remote fields.

