THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis responsible for the “high” users experience. When consumed, it binds to the body’s endocannabinoid receptors (primarily CB1 and CB2), which play vital roles in regulating mood, appetite, pain, and—interestingly—metabolism.
Your body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) helps maintain balance (homeostasis) across various bodily functions, including how your body stores fat and burns calories.
The Science: Does THC Really Increase Metabolism?
Emerging research has suggested a potential link between THC use and a faster metabolism. One study published in The American Journal of Medicine found that regular cannabis users had lower fasting insulin levels and smaller waist circumferences compared to non-users.
Other observational studies have shown that despite increased calorie intake due to the “munchies,” many cannabis users have lower body mass indexes (BMIs). This paradox has sparked curiosity about whether THC might indeed have a role in weight regulation and metabolic function.
Reasons Why THC Might Boost Metabolism
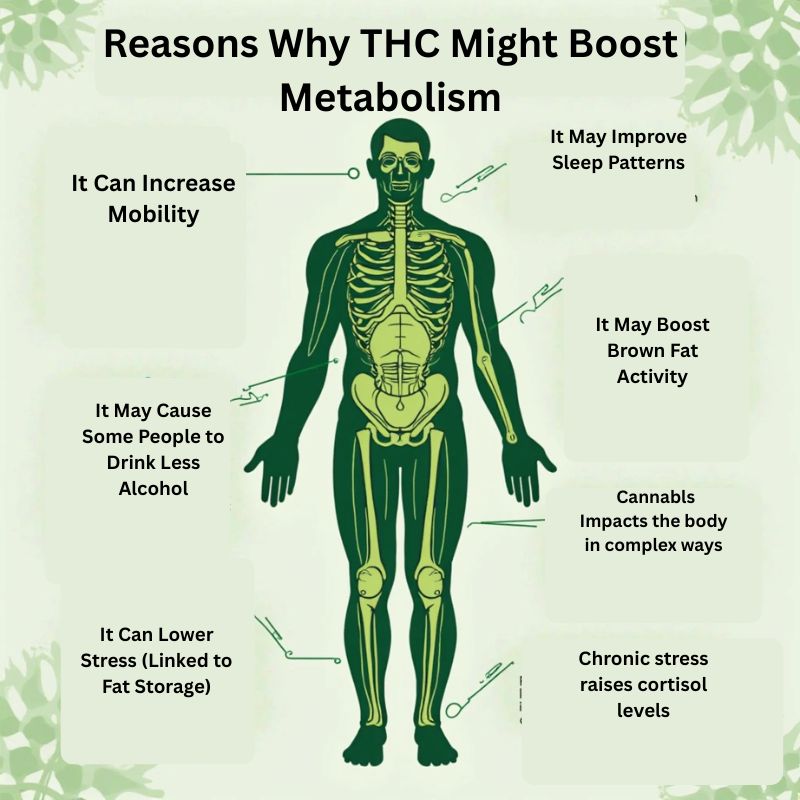
Cannabis impacts the body in complex ways. Here are some mechanisms researchers believe might contribute to increased metabolism:
It Can Increase Mobility
For individuals with chronic pain or inflammation, THC may promote movement by easing discomfort, indirectly boosting caloric burn through increased activity.
It May Cause Some People to Drink Less Alcohol
Some users substitute alcohol with cannabis, reducing their intake of calorie-rich beverages. This caloric deficit may influence weight changes over time.
It Can Lower Stress (Linked to Fat Storage)
Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which can promote fat storage, especially around the abdomen. THC’s anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) properties may help reduce cortisol, potentially aiding in fat metabolism.
It May Improve Sleep Patterns
Restorative sleep is essential for metabolic health. THC may help some individuals fall asleep faster or stay asleep longer, which can positively impact metabolic function.
It May Boost Brown Fat Activity
Brown adipose tissue (BAT), or “brown fat,” burns calories to generate heat. Some studies suggest cannabinoids can activate brown fat, thus supporting metabolism.
What About the Whole ‘Munchies’ Thing?
The most well-known side effect of THC is increased appetite, or the “munchies.” THC stimulates the release of ghrelin, the hunger hormone, which drives cravings—often for high-calorie, high-carb foods.
While THC might speed up metabolism in some people, this effect can easily be canceled out by overconsumption. The net effect depends on the balance between energy intake and expenditure.
Additionally, different cannabis strains have different effects:
- Sativa strains: More energizing; may promote movement and alertness.
- Indica strains: Sedating; can promote rest and hunger.
- Hybrids: Vary based on genetic lineage and cannabinoid content.
Does THC Help With Weight Loss?
While some evidence shows that cannabis users tend to weigh less than non-users, this doesn’t mean THC is a weight loss solution. Lower BMI may be correlated with lifestyle factors or strain-specific effects, not necessarily THC alone.
It’s also important to differentiate between weight loss (overall mass reduction) and fat loss (targeted reduction in body fat). THC might affect appetite and fat metabolism, but its effectiveness as a fat-burner is still unproven.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Like any substance, THC has risks, especially with long-term or high-dosage use:
- Unhealthy eating habits due to cravings
- Cognitive effects like memory impairment or reduced focus
- Potential dependency or psychological reliance
- Legal issues depending on your location
- Tolerance buildup which reduces its effects over time
THC also affects individuals differently. Age, gender, metabolic rate, and pre-existing conditions all play a role in how the body responds.
Safer Ways to Support Metabolism Naturally
Whether or not THC plays a role, proven ways to enhance metabolism remain vital:
- Strength training and HIIT workouts
- High-protein diet
- Proper hydration
- Sleep optimization
- Stress reduction
- Green tea, caffeine, or L-carnitine supplements
THC may complement some of these strategies but should not replace them.
Expert Opinions on THC and Metabolism
Health professionals remain cautious. Most agree that while cannabis may support metabolic balance in some indirect ways, more robust, large-scale studies are needed.
Some experts argue that the benefits seen in THC users could stem from other factors—such as improved sleep, pain relief, or stress management—not directly from increased metabolic activity.
The FDA does not currently approve THC for weight loss purposes.
Final Verdict: Can THC Speed Up Your Metabolism?
So, does THC speed up your metabolism? Possibly—but the answer isn’t black and white.
Some evidence suggests THC could modestly influence metabolism through appetite regulation, stress reduction, and increased activity. However, its effects vary widely and are counterbalanced by its ability to increase calorie intake.
👉 Unlock science-backed health tips and wellness insights at MindScribes — your trusted source for smarter living.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Does THC increase fat burning?
Some studies suggest THC can activate brown fat, which burns calories. However, clinical evidence remains limited.
Q2: Can smoking weed help you lose weight?
It may help reduce stress and improve sleep—both linked to better metabolism—but the increased appetite can cancel out any benefits.
Q3: What strains of cannabis boost metabolism?
Sativa strains, especially those high in limonene or pinene, may support alertness and activity, potentially aiding metabolism.

