As computing continues to evolve, the demand for more efficient and responsive systems has grown. One such advancement that revolutionized how we interact with computers is the time sharing operating system. This type of system enables multiple users to access a computer simultaneously without affecting each other’s experience. In this article, we will explore the essential properties of time sharing operating system, its benefits, and why it’s a fundamental concept in modern computing.
What Is a Time Sharing Operating System?
A time sharing operating system is a type of multitasking system that allows multiple users to use the same computer resources at the same time. Unlike batch processing or single-user systems, time sharing breaks up CPU time into small slots and allocates each slot to different users or processes. This creates the illusion that each user has their own dedicated machine, even though the system is switching rapidly between tasks.
The core idea behind this is time slicing—a technique where the CPU processes small pieces of multiple jobs in a rapid sequence, giving an almost instantaneous response to each user.
Essential Properties of Time Sharing Operating System
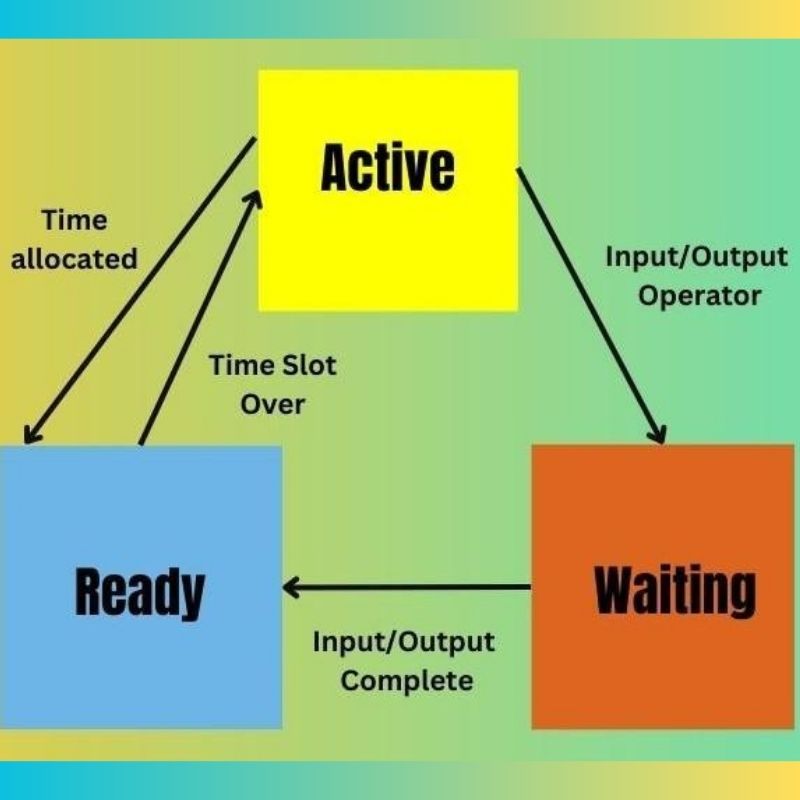
Understanding the essential properties of time sharing operating system is critical for students, IT professionals, and tech enthusiasts. These properties define the system’s efficiency, user experience, and performance under multi-user environments.
1. Multi-user Accessibility
One of the most defining features of a time sharing operating system is that it allows multiple users to work on the same system concurrently. Each user is given access to a terminal (either physical or virtual), and the system switches rapidly between users to ensure smooth operations.
Why it matters:
This property supports collaborative environments, remote access, and educational setups where resources are shared among many users.
2. Quick Response Time
The system is designed to respond to user inputs in real time or near real time. Time slices are typically short (milliseconds), which allows the CPU to switch quickly between tasks and provide immediate feedback.
Why it matters:
Fast response is critical for tasks that require user interaction such as online coding, simulations, and database queries.
3. CPU Scheduling and Time Slicing
Time sharing operating systems use complex scheduling algorithms to determine which task gets the CPU and for how long. Round-robin scheduling is a commonly used method where each process is given an equal time slot in rotation.
Why it matters:
Efficient CPU scheduling ensures fair use of system resources and prevents any single user or process from dominating the system.
4. Memory Management and Protection
Since multiple users are working simultaneously, the system must manage memory allocation effectively. It ensures that each user’s processes do not interfere with others, maintaining data integrity and system stability.
Why it matters:
This property is vital for security and efficiency. Without proper memory protection, one user’s process could potentially overwrite or access another’s data.
5. Security and Isolation
Each user’s data and applications are isolated from others. Time sharing systems use authentication, process isolation, and access control to prevent unauthorized access and maintain system integrity.
Why it matters:
Security becomes crucial when different users are working on the same system. Protecting user data builds trust and ensures compliance in multi-user environments.
These essential properties of time sharing operating system combine to create an efficient, fair, and responsive computing environment for multiple users at once.
Benefits of Time Sharing Systems
Time sharing operating systems offer numerous advantages across different sectors:
- Cost-effective Resource Use: Multiple users share system resources, reducing the need for separate machines.
- Increased Productivity: Users can work simultaneously without waiting for batch processes to complete.
- Real-time User Interaction: Enables immediate command execution and feedback.
- Scalability: Suitable for growing organizations or educational institutes with increasing user demands.
In modern systems, especially cloud computing and remote education platforms, these properties remain vital and applicable.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their advantages, time sharing systems come with a few challenges:
- System Overload: Too many simultaneous users may degrade performance.
- Security Risks: Without proper security protocols, data breaches can occur.
- Complex Management: Requires skilled administrators to manage user access, system load, and software updates.
However, with proper infrastructure and security in place, these challenges are manageable.
Use Cases of Time Sharing Systems
Time sharing operating systems are widely used in:
- Universities and Colleges: For programming labs, research, and administrative functions.
- Corporate IT Infrastructure: For shared development environments or hosted services.
- Cloud Platforms: Virtual machines and remote desktops rely on time-sharing principles.
- Government and Research Labs: Where secure and cost-effective computing is essential.
Understanding the essential properties of time sharing operating system is key to designing scalable and efficient systems in any of these areas.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main difference between time sharing and batch systems?
Time sharing provides immediate user interaction through time slicing, while batch systems process jobs without user involvement in real-time.
Q2. Is time sharing used in modern computing?
Yes. Cloud computing, virtual environments, and servers rely heavily on time-sharing principles to serve multiple users simultaneously.
Q3. What scheduling algorithm is most commonly used?
Round-robin scheduling is widely used due to its fairness and simplicity in distributing CPU time among users.
Q4. How does a time sharing system ensure data privacy?
By isolating memory spaces and using user-level authentication and access control policies.
Q5. Can time sharing operating systems be used in mobile devices?
While not common, some mobile OS features are inspired by multitasking principles similar to time sharing.
Conclusion
The essential properties of time sharing operating system form the backbone of many modern computing environments. With features like multi-user access, quick response time, robust memory management, and secure processing, these systems provide a foundation for interactive, scalable, and efficient computing.
Whether you’re a student exploring operating systems or a professional working on enterprise infrastructure, understanding these core principles helps you make better design, development, and deployment decisions.For more tech insights, educational guides, and career-oriented resources, explore MindScribes—your go-to platform for learning and growth in the digital age.

