An operating system (OS) is the essential software layer that bridges the gap between users and computer hardware. Whether you’re using Windows, macOS, Linux, or Android, the components of operating system work behind the scenes to ensure everything functions smoothly. Each component plays a unique and critical role in managing resources, executing programs, and providing a user interface.
This guide breaks down the main components of an operating system in simple terms while maintaining the technical depth necessary for students, tech enthusiasts, and IT professionals.
What is an Operating System?
Before diving into its components, it’s important to understand what an operating system actually is. An operating system is system software that manages hardware and software resources on a computer. It provides essential services to run application programs and controls hardware components like memory, CPU, and devices.
Common examples include Windows, Linux, macOS, Android, and iOS. Despite their differences, all these systems share core functionalities enabled by several key components.
Major Components of Operating System
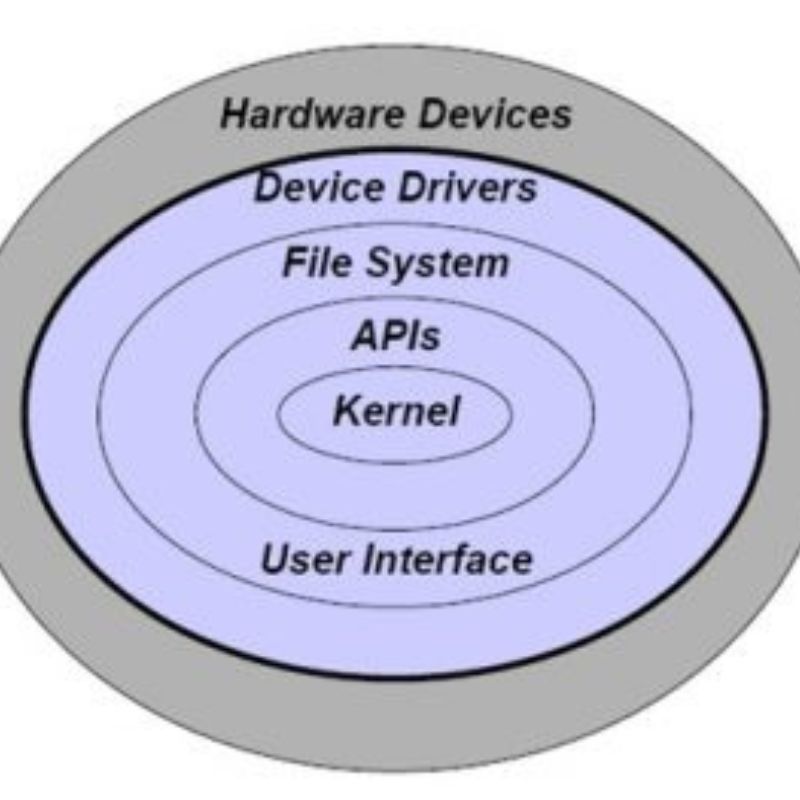
Each operating system is made up of multiple essential components that work together to ensure performance, security, and user experience. Let’s explore these main components in detail
1. Kernel
The kernel is the core of the operating system. It operates at the lowest level and is responsible for managing the system’s resources.
Key responsibilities:
- Managing CPU scheduling and multitasking
- Handling memory allocation and protection
- Managing input/output (I/O) operations
- Controlling device communication via drivers
Without the kernel, other components of the OS wouldn’t function. It acts as the central manager that coordinates all system activities.
2. Process Management
Process management handles the creation, scheduling, and termination of processes—the running instances of programs.
Main tasks include:
- Allocating CPU time among processes
- Managing process states (running, waiting, suspended)
- Handling inter-process communication (IPC)
- Preventing deadlocks and ensuring safe multitasking
This component ensures that multiple programs can run simultaneously without interfering with one another.
3. Memory Management
Memory management is essential to ensure each process gets enough memory without disrupting others.
Key functions:
- Allocating and deallocating memory space
- Keeping track of each byte in memory
- Managing virtual memory and swap space
- Preventing memory leaks and segmentation faults
By doing this, the OS maximizes efficiency and ensures data protection across processes.
4. File System Management
The file system is responsible for storing, retrieving, and organizing files on storage devices like HDDs, SSDs, or USBs.
Roles include:
- Creating, reading, writing, and deleting files
- Maintaining directories and subdirectories
- Managing access permissions and security
- Ensuring data integrity and backup support
Each operating system supports different file systems like NTFS (Windows), ext4 (Linux), or APFS (macOS).
5. Device Management
Device management oversees communication between the system and its hardware peripherals like keyboards, printers, monitors, and network cards.
Functions:
- Using device drivers to translate OS commands into hardware-specific language
- Managing input and output operations
- Handling errors or device failures gracefully
- Coordinating data flow between system and devices
The OS treats each device as a file, allowing standard access methods across different hardware.
6. User Interface (UI)
The user interface allows users to interact with the system. It can be either:
- Graphical User Interface (GUI): Visual elements like windows, icons, and menus (e.g., Windows, macOS)
- Command-Line Interface (CLI): Text-based interface where users type commands (e.g., Linux terminal, Command Prompt)
The UI enhances usability by making system operations accessible and manageable for both technical and non-technical users.
7. Security and Access Control
Security is a critical OS component designed to protect system resources and data from unauthorized access or threats.
Responsibilities:
- Enforcing authentication (passwords, biometrics)
- Providing user permissions and access levels
- Protecting against malware or system intrusions
- Enabling encryption and secure file transfer protocols
Modern operating systems are constantly updated with patches to strengthen security and fix vulnerabilities.
8. Networking
Most OS today are network-enabled, allowing systems to communicate over local or global networks.
Features include:
- TCP/IP protocol management
- Resource sharing (files, printers)
- Firewall configuration and data traffic monitoring
- Remote login and cloud integration support
This component is crucial for internet connectivity, file transfers, and cloud computing environments.
FAQs About Components of Operating System
1. What is the most important component of an operating system?
The kernel is considered the most essential part. It manages all core functions, from process and memory management to hardware control.
2. How does process management improve performance?
It ensures the CPU is used efficiently by assigning time slots, prioritizing tasks, and preventing resource conflicts.
3. What’s the difference between GUI and CLI?
GUI offers a visual interface, ideal for general users. CLI is text-based and preferred by advanced users for speed and flexibility.
4. Why is memory management critical?
Improper memory allocation can cause crashes, data loss, or slow performance. Memory management ensures stability and efficiency.
5. Are these components the same in mobile operating systems?
Yes, though simplified, mobile OS like Android or iOS include all core components like kernel, memory, file system, and user interface.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the components of operating system helps you appreciate how computers work behind the scenes. From managing memory and processes to enabling user interaction and security, each component plays a vital role in ensuring system stability, speed, and usability.
Whether you’re learning for exams, exploring computer science, or simply curious, this knowledge forms the foundation of modern computing.
Want more in-depth tech articles, simplified for better understanding?
Explore expert-written guides at MindScribes and enhance your knowledge in technology, programming, and system design.
Let me know if you’d like this content in visual format, PowerPoint, or as an infographic!

